· Glossary · 4 min read
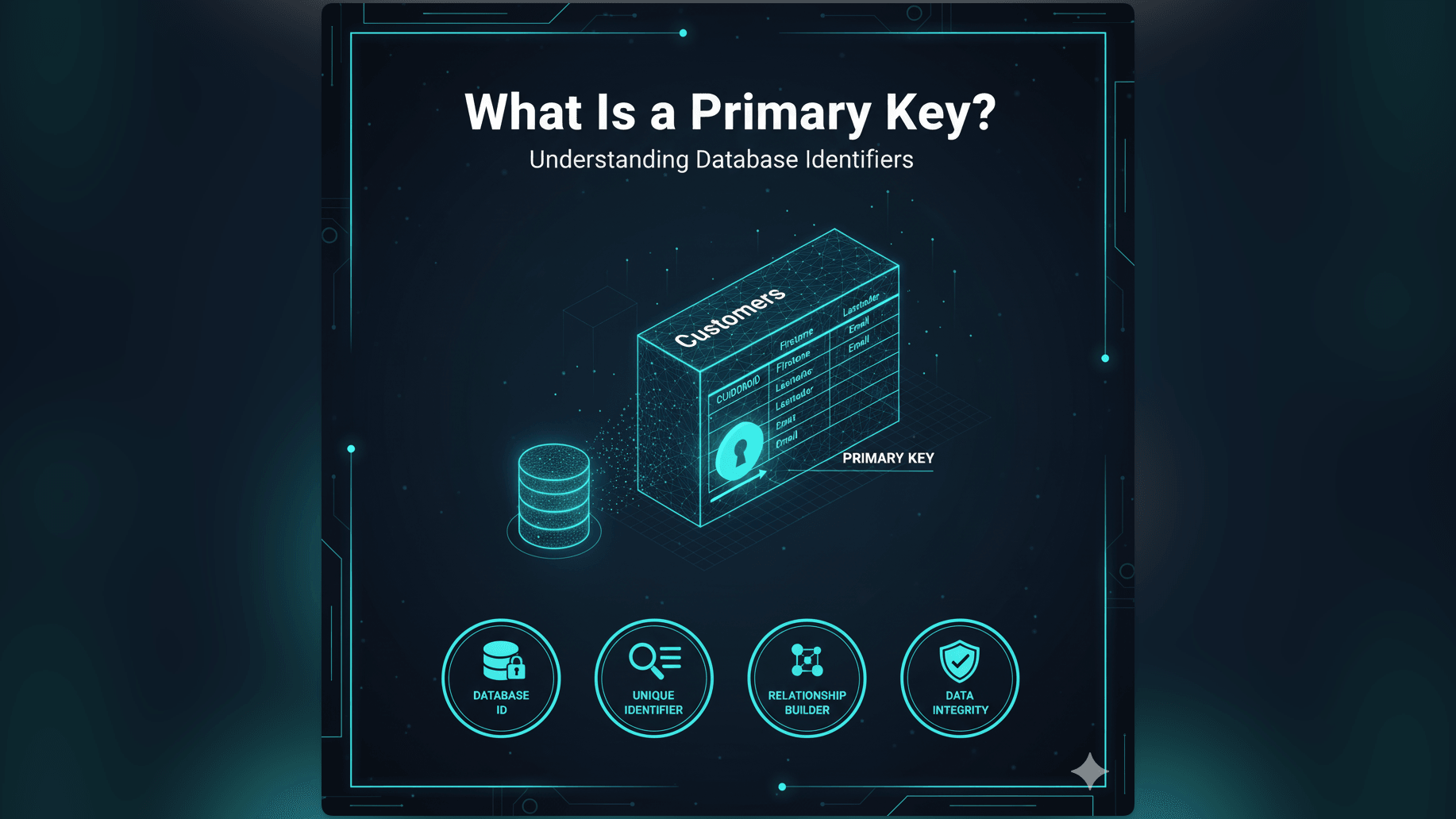
What Is a Primary Key?
A Primary Key is a unique identifier for records in a database table. Learn how primary keys ensure data integrity, facilitate relationships between tables, and improve search performance in database design.
Databases are designed to store massive amounts of information. But storing data is useless if you cannot find it again. A Primary Key is the tool that ensures you can always find exactly what you are looking for.
Simple Definition of a Primary Key
A Primary Key is a specific column or a set of columns in a database table that uniquely identifies each record.
Think of it like a fingerprint for data. Every person has a unique fingerprint: no two people share the same one. Similarly, in a database table, every row must have a unique Primary Key value.
There are two strict rules for a Primary Key:
- It must be unique: No duplicate values are allowed.
- It cannot be null: Every record must have a value.
Uniquely Identifying Records in a Database Table
If you have a table of “Users,” you cannot rely on names to distinguish them. There might be five people named “John Smith.” You cannot rely on email addresses because people might change them or share them.
The Primary Key provides a stable, guaranteed way to point to a specific “John Smith.” It is the fundamental address of that row.
Why Primary Keys Are Crucial for Database Integrity
Without Primary Keys, a relational database is just a messy pile of unstructured data.
Ensuring Uniqueness and Establishing Relationships
The most obvious job of a Primary Key is to prevent duplicates. It stops you from accidentally creating the same user account twice.
But its more important job is to act as an anchor. In a relational database, tables need to talk to each other. The Primary Key is the connecting point. If you want to link an “Order” to a “Customer,” the Order table will save the Customer’s Primary Key. This is how the database knows which customer bought which item. Without a Primary Key, you cannot create these relationships.
Essential for Data Retrieval and Management
Primary Keys also make databases fast. Because the database engine knows this column is unique, it creates an index for it. This means searching for a user by their ID is almost instantaneous, whereas searching by their name takes much longer.
Real-World Example: Customer ID as a Primary Key
Let’s look at an online store’s database. We have a Customers table:
- Row 1: John Doe, john@example.com
- Row 2: Jane Doe, jane@example.com
If we want to assign a Primary Key, we usually add a new column called CustomerID:
- Row 1: CustomerID 101
- Row 2: CustomerID 102
How a Unique Identifier Works
Now imagine John changes his email. Or imagine another John Doe signs up. It does not matter. The database tracks him as 101. When John makes a purchase, the Orders table simply records “Customer 101 bought a book.” It references the Primary Key. This keeps the data clean and consistent.
How AI Diagram Maker Recognizes Primary Keys in ERDs
Visualizing these keys is a critical part of database design. When you look at an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), you need to know which columns are the keys.
Automatically Highlighting Keys in Generated ER Diagrams
With our AI ER Diagram Generator, we make this visible instantly.
When you import your SQL code, our AI detects the PRIMARY KEY syntax. In the generated diagram, it places a special icon: usually a small key symbol or the letters “PK”: next to that column.
It also uses these keys to draw the connecting lines between tables. This allows you to see exactly how your data is linked, giving you a clear map of your database structure.
Related Terms
To understand database structures, you should know these related terms:
- Foreign Key: A column that points to the Primary Key of another table. It is the other half of the relationship link.
- ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram): The visual map that shows tables and how they link via keys. Read more about ERDs.
- Database Table: A collection of related data structured in rows and columns.
- Relational Database: A type of database that stores data in tables and uses keys to define relationships between them (like MySQL or PostgreSQL).
- Database Schema: The blueprint of how the database is constructed including all tables and keys.
For more on visualizing database schemas, check out our Developer’s Guide to AI Diagramming.