· Glossary · 2 min read
What Is Cardinality?
Cardinality defines the numerical relationship between rows in different tables within a database, specifying how many instances of one entity can be associated with instances of another.
When you design a database, connecting two tables is just the first step. The real question is “How many items connect to how many items?” Cardinality is the answer to that question.
Simple Definition
Cardinality refers to the numerical relationship between rows of one table and rows of another table. It defines the rules of the relationship. Does one Customer have exactly one Address? Or can they have five? Can an Order exist without a Customer? These rules determine how you write your SQL queries and how you structure your data storage.
Quantifying Relationships Between Data Entities
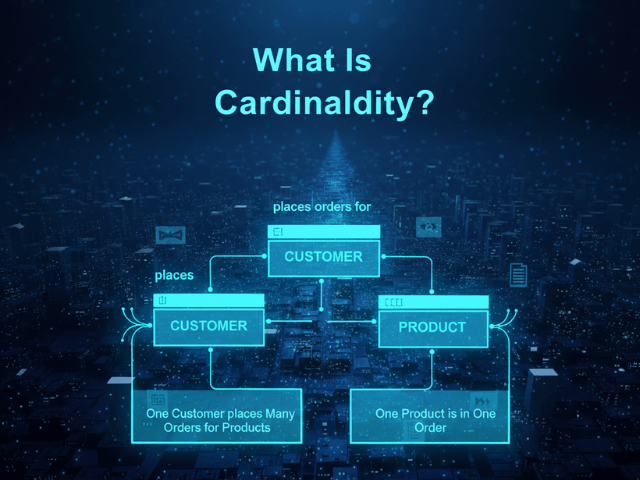
Think of it as the “Count.” If you are building a school system, you have Students and Classes. A Student takes Many classes. A Class has Many students. This “Many-to-Many” cardinality dictates that you need a special “Join Table” to link them. If you get the cardinality wrong, your database will not work.
Types of Cardinality
There are three main patterns you will see in every database.
One-to-One (1:1)
One record in Table A relates to one and only one record in Table B. Example: User and Passport. A user has one passport. A passport belongs to one user.
One-to-Many (1:N)
One record in Table A relates to zero, one, or many records in Table B. Example: Author and Books. One author can write many books. But a specific book is written by one author (simplifying for the example). This is the most common relationship.
Many-to-Many (M:N)
Many records in Table A relate to many records in Table B. Example: Students and Courses.
Visualizing Cardinality
You cannot just guess cardinality. You need to see it.
Using connector endings in ERDs
In an Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD), we use Crow’s Foot Notation to show cardinality. A simple line ending means “One.” A three-pronged fork ending means “Many.” Looking at these endings allows a developer to instantly understand the business rules. “Oh, I see the Crow’s Foot on the ‘Orders’ table. That means a User can place multiple orders.”
Related Terms
To master data modeling, you should know these terms.
- ERD: The diagram where cardinality is visualized.
- Crow’s Foot: The specific symbol used to denote “Many.”
- Database Schema: The structural definition of the database that enforces these cardinality rules via constraints.
- Foreign Key: The column that technically implements the One-to-Many relationship.
For more on automating your database diagrams, check out our Developer’s Guide: The Programmable Diagram: A Developer’s Guide to D2 and Text-Based Visuals.